Gene Prediction
EMBOSS: translation of nucleic acid into protein
The majority of protein sequences are derived from annotated nucleic acid sequences using a translation tool.
- Go to the EMBOSS home page
- Search the page for translation (using Ctrl + F)
- In the NUCLEIC TRANSLATION section in the left menu, click transeq

| Translate the CDS of the mouse basic domain/leucine zipper transcription factor L36435. |
|---|
If you did everything right you should obtain a protein sequence starting with a methionine (M) and ending with a *, which represents a stop codon. |
| Translate the CDS of the unknown human sequence that you can download here. |
|---|
| In this sequence you don't know where the CDS is located but you do know it's there. Fortunately you can use transeq to find a CDS without knowing in which frame you should look. To do this you can select 6 (All six fames) in the Parameters section of the tool to obtain all reading frames.
 |
Of course, this doesn't work when you start from a genomic sequence of a gene that contains introns. Translation tools do not take into account the presence of introns.
A good alternative for the EMBOSS Transeq tool is the Expasy Translate tool.
GENSCAN to predict eukaryotic genes
Translating DNA (see previous exercise) and gene prediction are two very different things.
The translation software will translate any DNA sequence that you feed it regardless of whether the DNA sequence really is a CDS or not. Gene prediction software on the other hand looks for sound evidence (base composition, similarity to known CDS, presence of motifs...) to predict the location of CDS in a DNA sequence.
The Genbank entry with accession number X02419 contains the sequence of the gene encoding the urokinase-type plasminogen activator. We will run gene prediction software on the sequence and see if the software manages to correctly find the CDS. GENSCAN is one of the most popular tools for gene searching. It is used by the genome annotation pipeline at EBI, while a slightly modified version (Gnomon) is used at NCBI.
GENSCAN models eukaryotic genes with HMMs (hidden markov models) for the:
- coding parts of eukaryotic exons
- TATA-box
- CAP-site
- polyA-site
The software offers these models for human (usable for all vertebrates), Arabidopsis thaliana and maize.
GENSCAN is available via the Mobyle portal. Go to the Mobyle home page.
- In the left menu expand sequence
- Expand nucleic
- Expand gene_finding
- Click genscan

In the Input section:
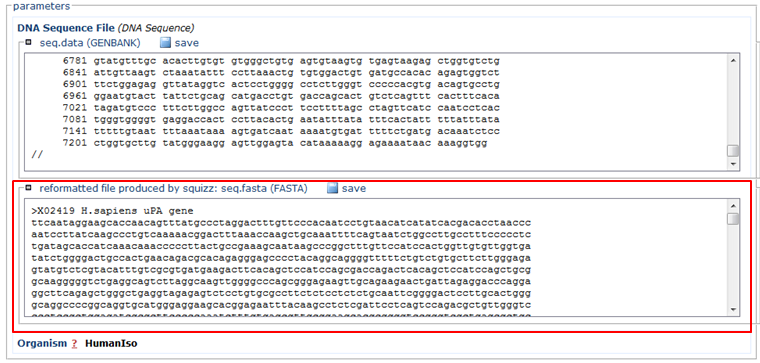
- Paste the sequence in FASTA format (red)
- In the Organism section, choose HumanIso (green)
- Click the Run button (blue)

The Mobyle server will ask for your email address, provide it and click Ok.
The Mobyle server will ask you to validate your submission, do so and click Ok.
You can compare the result with the annotation in the Genbank file of the sequence: it has Genbank accession X02419.
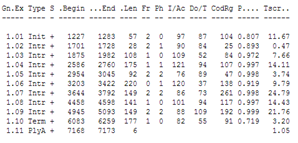
| Did GENSCAN predict the CDS correctly ? |
|---|
| You can choose to see the GENSCAN prediction full screen The Mobyle portal is not always working well so if it doesn't generate an output you can go to the genscan page at MIT. Copy the reformatted sequence from the Mobyle results page: and paste it in the GENSCAN page at MIT in the input sequence text box. Click Run Genscan. You get the same results as shown above for the Mobyle portal. The annotation of the Genbank file: You will see that GENSCAN correctly predicted the CDS. |
GENSCAN also found a polyA-site in the correct location. Note that GENSCAN does not find non-coding exons like the first exon in the Genbank file.